Memory Settings
The total amount of memory needed by SQL Server depends on your use case and (expected) workload. SQL Server will claim memory from the OS when needed but will not give it back to the OS once claimed. If no limit is specified you will run the risk of starving the host server and OS of enough free memory to operate efficiently. It is therefore strongly advised to limit the maximum amount SQL Server is allowed to use.
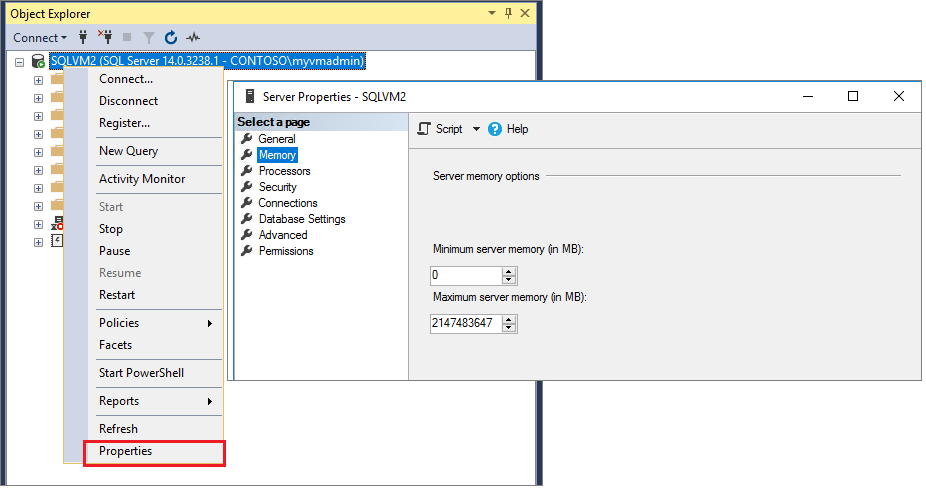
To set a fixed amount of memory using SSMS [1]:
In Object Explorer, right-click a server and select Properties.
Click the Memory node.
Under Server Memory Options, enter the amount that you want for ‘Minimum server memory (in MB)’ and ‘Maximum server memory (in MB)’.
Use the default settings to allow SQL Server to change its memory requirements dynamically based on available system resources. It is recommended to set a max server memory as detailed above.
Windows Server with Desktop Experience requires a minimum memory size of 2 GB [2], but 4 GB or more is recommended (more is better). Example: If your server has 64GB of memory, set the amount of memory in SQL Server to 60,000MB (i.e. 64GB - 4GB = 60GB)
